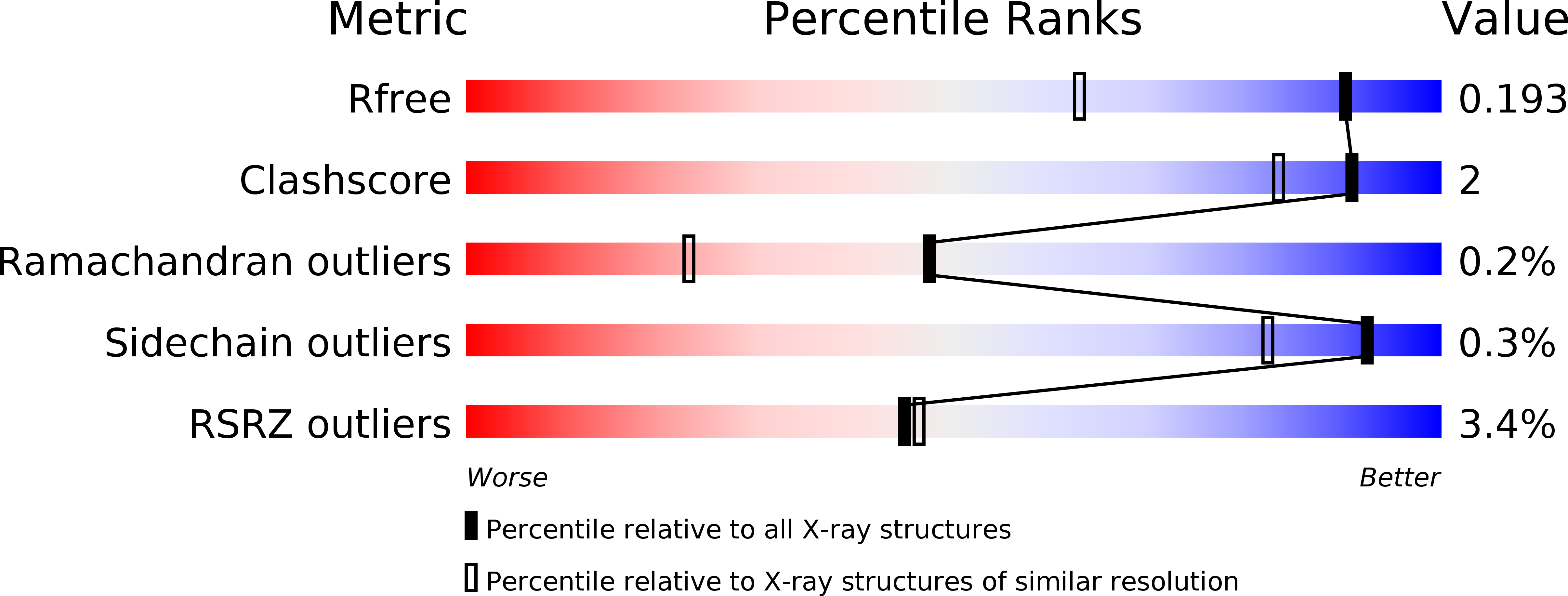
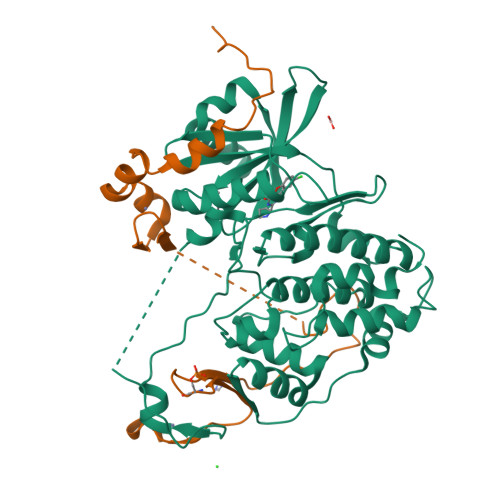
Structural Basis for the Activation and Target Site Specificity of CDC7 Kinase.
Dick, S.D., Federico, S., Hughes, S.M., Pye, V.E., O'Reilly, N., Cherepanov, P.(2020) Structure 28: 954-962.e4
- PubMed: 32521228
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2020.05.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6YA6, 6YA7, 6YA8 - PubMed Abstract:
CDC7 is an essential Ser/Thr kinase that acts upon the replicative helicase throughout the S phase of the cell cycle and is activated by DBF4. Here, we present crystal structures of a highly active human CDC7-DBF4 construct. The structures reveal a zinc-finger domain at the end of the kinase insert 2 that pins the CDC7 activation loop to motif M of DBF4 and the C lobe of CDC7. These interactions lead to ordering of the substrate-binding platform and full opening of the kinase active site. In a co-crystal structure with a mimic of MCM2 Ser40 phosphorylation target, the invariant CDC7 residues Arg373 and Arg380 engage phospho-Ser41 at substrate P+1 position, explaining the selectivity of the S-phase kinase for Ser/Thr residues followed by a pre-phosphorylated or an acidic residue. Our results clarify the role of DBF4 in activation of CDC7 and elucidate the structural basis for recognition of its preferred substrates.
Organizational Affiliation:
Chromatin Structure and Mobile DNA, The Francis Crick Institute, London NW1 1AT, UK.